(P0) llama_index
动机、参考资料、涉及内容
涉及内容: 本篇博客主要记录 llama_index 的整体框架, 并适量记录一些用例配以说明
不涉及内容: 过于细致的 prompt, rag 技巧
目录结构
TODO (初次看可以酌情跳过本节, 主要用于回顾): 子目录非常多, 但层数不深, 慢慢补全
总体概述
一个伪代码例子 (尽可能牵涉到重点 class)
store1 = Store1(...)
store2 = Store2(...)
# 实际常使用 from_defaults 这个 classmethod 来构造
storage_context = StorageContext(store1, store2)
llm = LLM(...)
embed_model = EmbedModel(...)
prompt_helper = PromptHelper(...)
transformation = Transformation(...)
# 实际常使用 from_defaults 这个 classmethod 来构造
service_context = ServiceContext(llm, embed_model, prompt_helper, transformation)
# 实际常使用 from_documents 这个 classmethod 来构造
index = Index(
documents,
storage_context=storage_context,
service_context=service_context,
...
)
query_engine: QueryEngine = index.as_query_engine()
query_engine.query("what is 1")
chat_engine: ChatEngine = index.as_chat_engine()
chat_engine.chat("2+2")
ServiceContext (TODO)
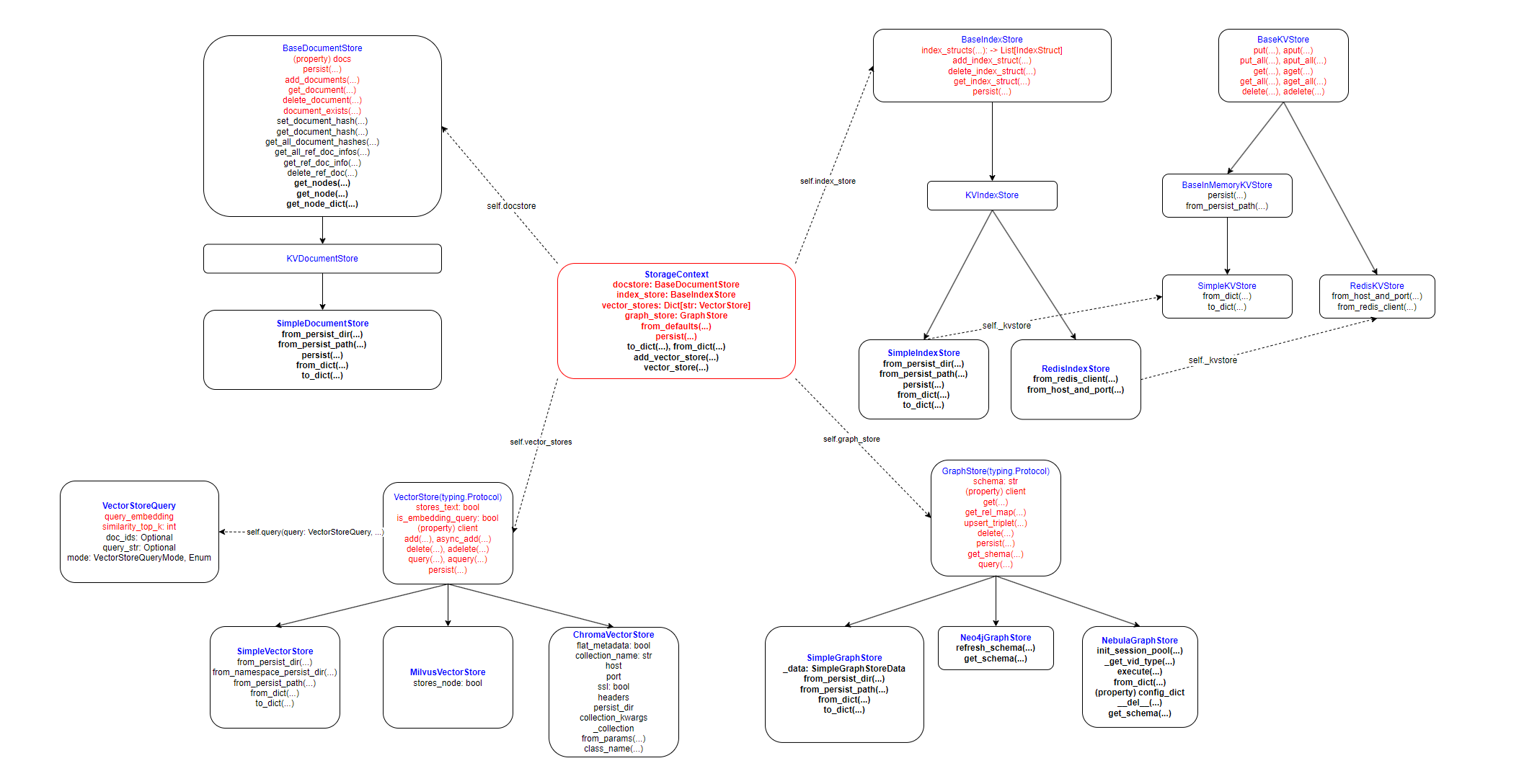
StorageContext
TODO: BaseKVStore 还包含 IndexStruct, 待加上
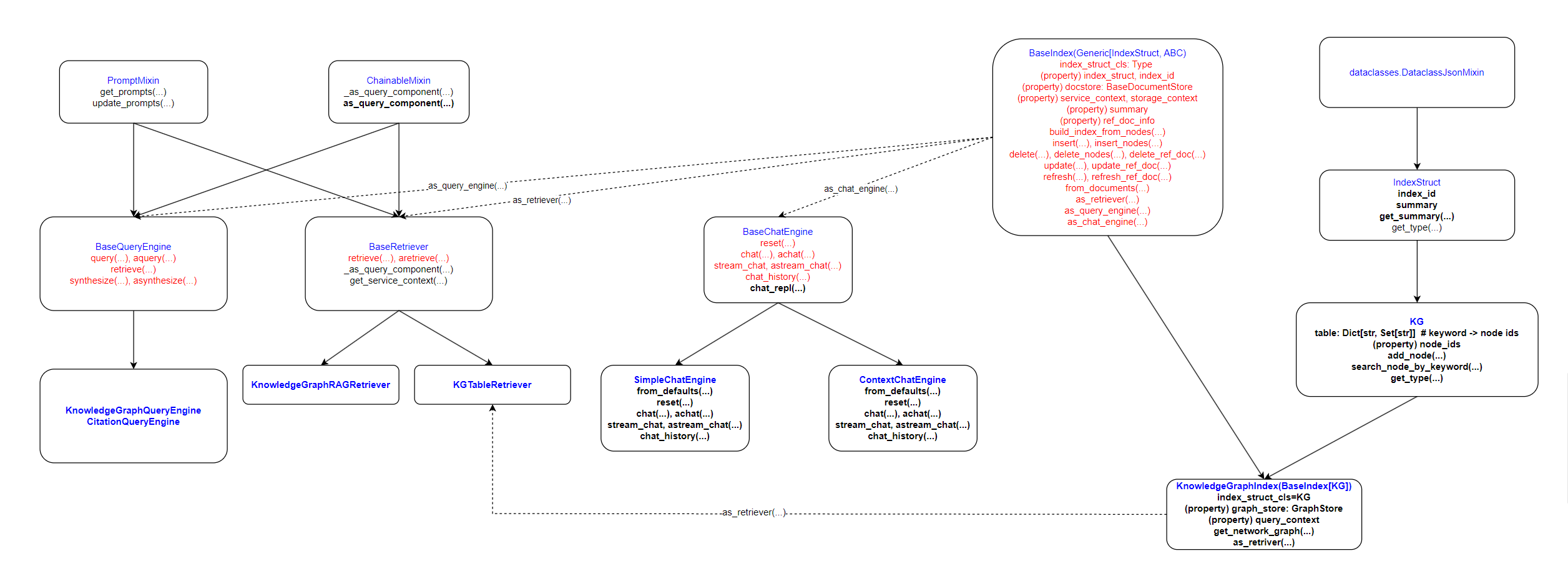
Index
TODO: index.as_chat_engine() 的返回结果也可能会是 BaseAgent, BaseAgent 同时继承自 BaseChatEngine 和 BaseQueryEngine
Demo 1: 探索 storage context
完整内容参见 https://github.com/BuxianChen/snippet/tree/master/llama_index/storage_context_example
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"
from llama_index import SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./txt_data").load_data()
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
print(index.to_dict())
storage_context = index.storage_context
storage_context.vector_store._data # SimpleVectorStore 特有方法, 返回所有向量
storage_context.vector_store.get('ef34824e-ae70-4a7e-a12d-a6092cdfe6ff') # 返回 embeding 向量: 长度为 1536 个浮点数的列表
模块
StorageContext
官方文档中大量存在 StorageContext.from_defaults 的使用, StorageContext 本质上只是一个字典, 没有更多东西
from llama_index.storage.storage_context import StorageContext
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(graph_store=graph_store)
llama_index.storage.Storage 的源代码 (v0.9.27) 如下:
# llama_index/storage/storage_context.py
DEFAULT_PERSIST_DIR = "./storage"
IMAGE_STORE_FNAME = "image_store.json"
IMAGE_VECTOR_STORE_NAMESPACE = "image"
@dataclass
class StorageContext:
docstore: BaseDocumentStore
index_store: BaseIndexStore
vector_stores: Dict[str, VectorStore]
graph_store: GraphStore
@classmethod
def from_defaults(
cls,
docstore: Optional[BaseDocumentStore] = None,
index_store: Optional[BaseIndexStore] = None,
vector_store: Optional[Union[VectorStore, BasePydanticVectorStore]] = None,
image_store: Optional[VectorStore] = None,
vector_stores: Optional[Dict[str, Union[VectorStore, BasePydanticVectorStore]]] = None,
graph_store: Optional[GraphStore] = None,
persist_dir: Optional[str] = None,
fs: Optional[fsspec.AbstractFileSystem] = None,
) -> "StorageContext":
if persist_dir is None:
docstore = docstore or SimpleDocumentStore()
index_store = index_store or SimpleIndexStore()
graph_store = graph_store or SimpleGraphStore()
image_store = image_store or SimpleVectorStore()
if vector_store:
vector_stores = {DEFAULT_VECTOR_STORE: vector_store}
else:
vector_stores = vector_stores or {DEFAULT_VECTOR_STORE: SimpleVectorStore()}
if image_store:
vector_stores[IMAGE_VECTOR_STORE_NAMESPACE] = image_store # append image store to vector stores
else:
docstore = docstore or SimpleDocumentStore.from_persist_dir(persist_dir, fs=fs)
index_store = index_store or SimpleIndexStore.from_persist_dir(persist_dir, fs=fs)
graph_store = graph_store or SimpleGraphStore.from_persist_dir(persist_dir, fs=fs)
if vector_store:
vector_stores = {DEFAULT_VECTOR_STORE: vector_store}
elif vector_stores:
vector_stores = vector_stores
else:
vector_stores = SimpleVectorStore.from_namespaced_persist_dir(persist_dir, fs=fs)
if image_store:
vector_stores[IMAGE_VECTOR_STORE_NAMESPACE] = image_store # append image store to vector stores
return cls(docstore=docstore, index_store=index_store, vector_stores=vector_stores, graph_store=graph_store,)
def to_dict(self) -> dict: ... # 略
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, save_dict: dict) -> "StorageContext": ... # 略
@property
def vector_store(self) -> VectorStore: ... # 略
def add_vector_store(self, vector_store: VectorStore, namespace: str) -> None:
self.vector_stores[namespace] = vector_store
我们可以看到, StorageContext 的重点在于以下四类 Store, StorageContext.from_defaults 方法对这 4 类 Store 的默认类如下:
docstore: BaseDocumentStore:SimpleDocumentStoreindex_store: BaseIndexStore:SimpleIndexStorevector_stores: Dict[str, VectorStore]:SimpleVectorStoregraph_store: GraphStore:SimpleGraphStore
持久化保存 (TODO: Unclear)
例子:
# llama_index==0.9.16
from llama_index import StorageContext, ServiceContext
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex
persist_dir = "./index"
origin_dir = "./data"
if os.path.exists(persist_dir):
document = []
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir=persist_dir)
# Method 1:
# Error: storage_context.vector_store.stores_text is False
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(
vector_store=storage_context.vector_store,
service_context=service_context
)
index.storage_context = storage_context
# Method 2:
# Error: No documnet
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_document(
document = [],
service_context=service_context,
storage_context=storage_context
)
# Method 3: OK
# 跟 Method 4 一致: storage_context.index_store.index_structs() is a list
index = VectorStoreIndex(
index_struct = storage_context.index_store.get_index_struct(),
service_context=service_context,
storage_context=storage_context
)
# Method 4: OK
index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context=storage_context, service_context=service_context)
else:
# OK
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(origin_dir).load_data() # List[Document]
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults()
index = from_document(
documents = documents,
service_context=service_context,
storage_context=storage_context
)
# 也可直接转换为 as_query_engine, as_chat_engine
# https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/understanding/querying/querying.html
retriever = index.as_retriever()
retriever.retrieve("xxx")
内部细节:
load_index_from_storage的本质是使用storage_context.index_store获取其内部的IndexStruct构造函数所需的参数, 从而先构造出IndexStruct, 然后再用这个IndexStruct构造出IndexStoreIndexStore包含KVStore,KVStore又包含IndexStruct
def load_index_from_storage(storage_context, ...):
indices = load_indices_from_storage(...)
assert len(indices) == 0
return indices[0]
def load_indices_from_storage(storage_context, index_ids=None, **kwargs):
if index_ids is None:
index_structs = storage_context.index_store.index_structs()
else:
index_structs = [storage_context.index_store.get_index_struct(index_id) for index_id in index_ids]
indices = []
for index_struct in index_structs:
# type_: IndexStructType.VECTOR_STORE, 即字符串 "vector_store"
type_ = index_struct.get_type() # index_struct: IndexDict
index_cls = llama_index.indices.registry.INDEX_STRUCT_TYPE_TO_INDEX_CLASS[type_] # index_cls: VectorStoreIndex
index = index_cls(
index_struct=index_struct, storage_context=storage_context, **kwargs
)
indices.append(index)
return indices
def json_to_index_struct(struc_dict):
type = struct_dict["__type__"] # type 是 llama_index.data_structs.data_structs.IndexDict, 继承自 IndexStruct
cls = llama_index.index_structs.registry.INDEX_STRUCT_TYPE_TO_INDEX_STRUCT_CLASS[type]
data_dict = struct_dict["__data__"] # 实际上是 str
return cls.from_json(data_dict) # `from_json` 是 from json dict str, 这个构造方法只是普通的变量赋值
class KVIndexStore(BaseIndexStore): # SimpleIndexStore 继承自 KVIndexStore
def index_structs(self):
# self._kvstore 是 SimpleKVStore, 它简单来说是一个字典 (这个字典实际上保存在 self._kvstore._data 中)
# {"collection_id": {"struct_id": {"__type__": "vector_store", "__data__": "{...}"}}}
# 一个 collection 有一个或多个 index_struct
jsons = self._kvstore.get_all(collection=self._collection)
return [json_to_index_struct(json) for json in json.values()]
def index_struct(self, struct_id):
json = self._kvstore.get(struct_id, collection=self._collection)
return json_to_index_struct(json)
GraphStore
继承关系:
typing.Generic -> typing.Protocol -> llama_index.graph_stores.types.GraphStore (抽象类) -> llama_index.graph_stores.Neo4jGraphStore (对 neo4j-python 的简单包装, 不涉及大模型)
使用 Neo4jGraphStore |
直接使用原生的 neo4j |
结果:
[
['SAID','she would like to see Gamora portrayed as "the most lethal woman in the galaxy"'],
['SAID', 'she would like to see Gamora rejoin the Guardians'],
['SAID', "Gamora's fate would depend on the plans that Marvel and Gunn have for Vol. 3"],
['RETURNED', 'to play a younger version in Endgame'],
['ASKED_ABOUT', 'her role in the film'],
['SIGNED_TO_PLAY', 'Gamora in one film'],
['STATED_THAT', 'Vol. 3 would be the final time she would portray Gamora']
]
ServiceContext
ServiceContext 也类似于 StorageContext, 仅仅是 LLM, PromptHelper, Embedding Model, transformations 的集合
@dataclass
class ServiceContext:
llm_predictor: BaseLLMPredictor
prompt_helper: PromptHelper
embed_model: BaseEmbedding
transformations: List[TransformComponent]
llama_logger: LlamaLogger # 准备弃用
callback_manager: CallbackManager
# 入参与field的对应关系见注释
@classmethod
def from_defaults(
cls,
llm_predictor: Optional[BaseLLMPredictor] = None, # 准备弃用参数, 使用 llm 参数: llm_predictor
llm: Optional[LLMType] = "default", # llm_predictor
prompt_helper: Optional[PromptHelper] = None, # prompt_helper
embed_model: Optional[Any] = "default", # embed_model
node_parser: Optional[NodeParser] = None, # transformation
text_splitter: Optional[TextSplitter] = None, # transformation
transformations: Optional[List[TransformComponent]] = None,# transformation
llama_logger: Optional[LlamaLogger] = None, # llama_logger
callback_manager: Optional[CallbackManager] = None, # callback_manager, transformation
system_prompt: Optional[str] = None, # llm_predictor
query_wrapper_prompt: Optional[BasePromptTemplate] = None, # llm_predictor
# pydantic program mode (used if output_cls is specified)
pydantic_program_mode: PydanticProgramMode = PydanticProgramMode.DEFAULT, # llm_predictor
# node parser kwargs
chunk_size: Optional[int] = None, # transformation
chunk_overlap: Optional[int] = None, # transformation
# prompt helper kwargs
context_window: Optional[int] = None, # prompt_helper
num_output: Optional[int] = None, # prompt_helper
# deprecated kwargs
chunk_size_limit: Optional[int] = None, # 准备弃用参数, 使用 chunk_size 参数: transformation
) -> "ServiceContext": ... # 略
# 其余均略去
LLM, Embedding Model
LLM 的继承关系主要是: BaseLLM -> LLM -> OpenAI, 主要方法是 chat, complete (以及对应的 stream/async 方法), 而 predict (以及 stream 和对应的 async 方法) 方法实际上是根据 self.metadata.is_chat_model 的取值回归到 chat 或 complete 上来, 而 chat 与 complete 就只是分别对应 ChatCompletion 和 Completion 的 OpenAI API 接口.
PromptTemplate
PromptTemplate 的继承关系主要是: BasePromptTemplate -> PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate, SelectorPromptTemplate, LangchainPromptTemplate, 其中最主要的方法是:
get_template: 返回 str 类型, 用于查看 promptformat: 返回 str 类型, 用于将输入数据及 prompt 模板转换为送入 CompletionLLM 的输入format_messages: 返回 str 类型, 用于将输入数据及 prompt 模板转换为送入 ChatLLM 的输入
一些比较骚的操作可以参考: https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/examples/prompts/advanced_prompts.html
TextNode (Node), Document
基本上就是带一些验证逻辑的 pydantic.v1.BaseModel, 用了几层的继承: pydantic.v1.BaseModel -> BaseComponent -> BaseNode -> TextNode -> Document, 这里只简单看下字段
# BaseComponent: 没有字段
# BaseNode:
id_: str = Field(default_factory=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()), description="Unique ID of the node.")
embedding: Optional[List[float]] = Field(default=None, description="Embedding of the node.")
metadata: Dict[str, Any] = Field(default_factory=dict, description="A flat dictionary of metadata fields", alias="extra_info",)
excluded_embed_metadata_keys: List[str] = Field(default_factory=list, description="Metadata keys that are excluded from text for the embed model.",)
excluded_llm_metadata_keys: List[str] = Field(default_factory=list, description="Metadata keys that are excluded from text for the LLM.",)
relationships: Dict[NodeRelationship, RelatedNodeType] = Field(default_factory=dict, description="A mapping of relationships to other node information.",)
hash: str = Field(default="", description="Hash of the node content.")
# TextNode (Node = TextNode)
text: str = Field(default="", description="Text content of the node.")
start_char_idx: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, description="Start char index of the node.")
end_char_idx: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, description="End char index of the node.")
text_template: str = Field(default=DEFAULT_TEXT_NODE_TMPL, description="Template for how text is formatted, with {content} and {metadata_str} placeholders.",)
metadata_template: str = Field(default=DEFAULT_METADATA_TMPL, description="Template for how metadata is formatted, with {key} and {value} placeholders.",)
metadata_seperator: str = Field(default="\n", description="Separator between metadata fields when converting to string.",)
# Document:
id_: str = Field(default_factory=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()), description="Unique ID of the node.", alias="doc_id",)
_compat_fields = {"doc_id": "id_", "extra_info": "metadata"}
metadata 用于存储元信息, 例如使用 documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data() 时, 返回的每一个 Document 会包含文件位置, 文件大小, 创建时间等元信息
text_template = "{metadata_str}\n\n{content}" # DEFAULT_TEXT_NODE_TMPL
metadata_template = "{key}: {value}" # DEFAULT_METADATA_TMPL
metadata_seperator = "\n"
class MetadataMode(str, Enum):
ALL = auto()
EMBED = auto()
LLM = auto()
NONE = auto()
# Document.get_content 函数的主体内容
# 与 MetadataMode 有关, 如果是 ALL, 则会使用所有的 matadata, 如果是 EMBED, 则不使用 excluded_embed_metadata_keys, 如果是 None, 则 metadata_str 为空字符串
matadata_str = "\n".join([metadata_template.format(key=key, value=str(value)) for key, value in self.metadata])
content = text_template.format(metadata_str=metadata_str, content=self.text) if metadata else self.text
relationships 字段适用于后续从 Document 中分割出 Node, 用于表示节点与节点间的关系
class NodeRelationship(str, Enum):
SOURCE = auto() # "1", NodeRelationship.SOURCE == "1"
PREVIOUS = auto() # "2"
NEXT = auto() # "3"
PARENT = auto() # "4"
CHILD = auto() # "5"
class RelatedNodeInfo(BaseComponent):
node_id: str
node_type: Optional[ObjectType] = None
metadata: Dict[str, Any] = Field(default_factory=dict)
hash: Optional[str] = None
@classmethod
def class_name(cls) -> str:
return "RelatedNodeInfo"
RelatedNodeType = Union[RelatedNodeInfo, List[RelatedNodeInfo]]
relationships = {
NodeRelationship.SOURCE: RelatedNodeInfo(...), # 来源只能有一个
NodeRelationship.PREVIOUS: RelatedNodeInfo(...), # 在原始文本的前一个 chunk
NodeRelationship.NEXT: RelatedNodeInfo(...), # 在原始文本的后一个 chunk
NodeRelationship.PARENT: RelatedNodeInfo(...), # 父节点只能有一个, 什么是父节点?
NodeRelationship.CHILD: [RelatedNodeInfo(...), ...] # 子节点可以有若干个, 什么是子节点?
}
@property
BaseNode.[source_node,previous_node,next_node,parent_node,child_nodes]
Index, QueryEngine, Retriever, ChatEngine, Agent
ResponseMode
index.as_query_engine() 或 index.as_chat_engine() 时实际上会默认设置这个
llama_index.response_synthesizeers.type.PesponseMode, llama_index.get_response_synthesize
# get_response_synthesize 实现里可以看出这种对应关系, 位于 llama_index/response_synthesize
modes = [
"refine", # Refine
"compact", # CompactAndRefine
"simple_summarize", # SimpleSummarize
"tree_summarize", # TreeSummarize
"generation", # Generation
"no_text", # CompactAndAccumulate
"accumulate" # Accumulate
"compact_accumulate" # NoText
]
ChatMode
index.as_chat_engine() 时会设置这个
llama_index.chat_engine.types.ChatMode
# BaseIndex.as_chat_engine 的实现可以看出这种对应关系: llama_index/agent/*.py, llama_index/chat_engine/*.py
modes = [
"simple", # SimpleChatEngine
"condense_question", # CondenseQuestionChatEngine
"context", # ContextChatEngine
"condense_plus_context", # CondensePlusContextChatEngine
"react", # ReActAgent
"openai", # OpenAIAgent, 适用于支持 function_call 的模型, 大部分大模型不支持
"best", # 自动决定, 但只会回落到 react 和 openai, 这说明官方觉得用 react 比较 OK?
]
KnowledgeGraphIndex
用法可参考这个 Colab https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tLjOg2ZQuIClfuWrAC2LdiZHCov8oUbs#scrollTo=AQp9z4hRqNpy 以及参考根据以上 Colab 的整理 https://github.com/BuxianChen/material/tree/master/project/llama_index (目前为私有库, 待后续挪至 snippet 仓库)
可视化
- Simple: 打印
- DeepEval: 似乎需要登录
- Weights and Biases Prompts: 似乎需要登录
- OpenLLMetry: 需要登录
- Arize Phoenix: 可以本地部署
- OpenInference: ??
- TruEra TruLens: ??
- HoneyHive: ??
- PromptLayer: ??
实现上是通过 hook 机制来实现的, (TODO, 以 Arize Phoenix 为例)
未归类的杂录
默认 Prompt: https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index/blob/v0.9.30/llama_index/prompts/default_prompts.py