(P0) Pytorch Quantization
(Alpha) 总览
动机
了解模型量化的基本原理, 以及 Pytorch 对这些量化算法的实现
参考资料
- [A1] Pytorch 的一篇指导性的博客 (食用指南! 可快速上手使用转化为生产力, 读者如果仅出于使用目的可以只看这篇博客, 本文后续内容均可不看): https://pytorch.org/blog/quantization-in-practice/
- [A2] 官方支持量化的博客 (内含 3 种量化模式的上层 API, 但不是完整可运行示例, 也不包括后续版本增加的 fx mode 量化): https://pytorch.org/blog/introduction-to-quantization-on-pytorch/
- [A3] 官方文档 (需要仔细琢磨): https://pytorch.org/docs/2.1/quantization.html
- [A4] 官方 API 文档 (因为 Pytorch 提供了 3 种量化方式, 以及 eager/fx 模式, 并且 API 分为上层 API 和底层 API, 所以显得比较混乱, 个人还感觉 Pytorch 量化方面暴露的底层接口似乎不算完善): https://pytorch.org/docs/2.1/quantization-support.html
- [A5] Huggingface Optimum 的一篇关于模型量化的总览介绍: https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/v1.16.1/en/concept_guides/quantization
- [A6] Pytorch wiki (包含了关于底层诸如
torch.qint8数据类型的张量的一些 API): https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/wiki/Introducing-Quantized-Tensor - [A7] 一篇详细介绍数学公式推导的博客, 非常值得仔细研究: https://leimao.github.io/article/Neural-Networks-Quantization/
Pytorch Tutorials: 一些端到端的例子
- 官方 tutorial 搜索 (端到端的示例): https://pytorch.org/tutorials/search.html?q=quantization&check_keywords=yes&area=default
- Static Quantization + QAT: https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/static_quantization_tutorial.html
相关内容 (本文可能不会过多涉及):
- QLoRA: https://huggingface.co/blog/4bit-transformers-bitsandbytes
- FP8 paper: FP8 formats for deep learning: 英伟达 H100 引入, 文中写 E4M3 的最大值是 448, 但笔者按 IEEE 754 算是 240, 其余均吻合. 原因是 E4M3 不完全遵循 IEEE 754, 而 E5M2 遵循 IEEE 754 (参考: 博客)
- 一篇关于 QAT 的知乎博客, 博客中有原论文及原Tensorflow实现的, Pytorch 的实现包含在本文内容中. 如果要分析 QAT 的原始 TensorFlow 实现, 主要看这个端到端的例子, 以及入口源码, 这些代码与博客中的分析也基本一致.
- 一篇基于Pytorch官方博客的笔记: 博客园笔记
各种量化方法的推理流程
我们一般将中间结果称为 activation, 即每一层的输入/输出. Pytorch 原生量化支持有三类, 我们先看它们在推理阶段的计算流程, 参考自 A3:
Post-Training Dynamic Quantization
原理上是提前将权重转化为 int8. 在计算时, 每一层的输入 (activation) 先由浮点数转化为 int8 (activation 的量化过程动态进行: 例如用输入数据的 max_val 和 min_val 确定量化过程的放缩因子与零点, 由此再将 activation 转化为 int8 类型), 之后用 int8 的类型的输入与 int8 的权重进行矩阵乘法或卷积等运算得到结果, 然后将结果转换回浮点数. 因为每一层都需要动态计算出 max_val 和 min_val, 并且需要不断地对 activation 进行 int8 与浮点数之间的转换, 因此加速并不明显.
# original model
# all tensors and computations are in floating point
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_fp32 -- activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_fp32
# dynamically quantized model
# linear and LSTM weights are in int8
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_int8_w_fp32_inp -- activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_int8
Post-Training Static Quantization
原理上是模型训练好后, 首先将权重转换为 int8, 然后给模型喂入一批数据, 计算每层输入 (activation) 的分布情况, 由此得到每一层输入及输出的量化放缩因子与零点 (例如通过统计 max_val 和 min_val 做到), 模型推理过程如下: 每一层的输入都是 int8 类型, 然后直接与 int8 权重进行 int8 矩阵乘法等运算, 并根据输出的放缩因子进行少量的取整操作得到 int8 的输出 (可参见 A7 里的公式). 另外, 整个模型的输入层需要做一次 float 到 int 的静态量化, 输出层需要做一次反量化得到结果.
# original model
# all tensors and computations are in floating point
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_fp32 -- activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_fp32
# statically quantized model
# weights and activations are in int8
previous_layer_int8 -- linear_with_activation_int8 -- next_layer_int8
/
linear_weight_int8
Quantization Aware Training
在模型的训练过程中就模拟量化过程, 量化后的模型可以是 dynamic/static/weight-only 量化的 (按英文术语说是: QAT for dynamic/static/weight-only quantization), 因此对于推理来说, 与 dynamic/static/weight-only 没有区别, 而在训练过程中插入一些 Quant-DeQuant 过程
\[\hat{x} = f_d(f_q(x, s,z), s, z) = s(clip(round(\frac{x}{s}+z), a, b)-z)\]其中 $x$ 是原始数据, $\hat{x}$ 是经过量化-反量化操作后的结果 (浮点数), $s$ 是量化放缩系数 (浮点数), $z$ 是量化零点 (整数, 代表浮点数 0.0 的量化表示), $round$ 是取整函数, $clip$ 是截断函数, $a, b$ 代表量化值的整数表示最大值与最小值 (整数), $\alpha, \beta$ 则代表 $a, b$ 对应的反量化值 (浮点数), 上述量化反量化算子的近似梯度如下:
\[\frac{\partial{\hat{x}}}{\partial{x}} = \begin{cases} 1,\quad \alpha \leq x \leq \beta \\ 0,\quad otherwise \\ \end{cases}\]关于梯度计算参考 A7, 以下体现了 QAT for static quantization 的情况:
# original model
# all tensors and computations are in floating point
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_fp32 -- activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_fp32
# fq 代表一次量化加一次反量化过程, 因此 fq 的输出仍然是浮点数
# model with fake_quants for modeling quantization numerics during training
previous_layer_fp32 -- fq -- linear_fp32 -- activation_fp32 -- fq -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_fp32 -- fq
# quantized model
# weights and activations are in int8 (same as static quantization)
previous_layer_int8 -- linear_with_activation_int8 -- next_layer_int8
/
linear_weight_int8
需要注意的是, 还存在着另一个术语:
Weight-Only Quantization
原理是只对权重进行量化, 在计算时, 每一层的输入是浮点数, 权重被反量化会浮点数, 然后直接执行浮点数的算子得到结果. 因此这种量化方式在计算时实际上都是浮点运算.
# original model
# all tensors and computations are in floating point
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_fp32 -- activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_fp32
# Weight-Only Quantization
# weights are in int8, activations are in float
previous_layer_fp32 -- linear_with_activation_fp32 -- next_layer_fp32
/
linear_weight_int8 -- dequantized_linear_weight_fp32
使用
参考这个示例: https://github.com/BuxianChen/snippet/blob/master/quantization/quant_methods_compare.py
注意事项与 FAQ
Pytorch 的量化功能目前仅支持 CPU.
量化类型与计算时的累积类型 A5
- float16, accumulation data type float16
- bfloat16, accumulation data type float32
- int16, accumulation data type int32
- int8, accumulation data type int32
float32 -> float16 时 LayerNorm 的 eps 怎么办?
static quantization/QAT 使用注意事项 (即需要对原模型的代码进行变动, 例如增加 QuantStub 和 DeQuantStub 层, 使用 FloatFunctional 替换一些 add, cat 操作): A3-model-preparation-for-eager-mode-static-quantization
fx mode 与 eager mode:
- eager mode 需要使用者对原模型的代码进行上述小变动或重构, 而更理想的方式是不对原模型的代码进行变动, fx mode 可以实现这一点.
- eager mode 的
fuse_modules这一步需要手工指定需要 fuse 哪些层, 这需要使用者深入原模型代码细节去看哪些子模块需要被 fuse, 较难使用, 而 fx mode 可以避免这一点
(Alpha) API 总览
本节主要梳理 pytorch 关于量化的源码目录及 API 接口的层次关系, 尤其关注上层接口, 主要是梳理 A4, 但绝非完整介绍
源码位置
- Python 代码主要位于
torch/ao/nn和torch/ao/quantization, Pytorch 早期版本则位于torch.nn和torch/quantization, 为了保持兼容性, Pytorch 后续版本在这些目录的 Python 脚本里只包含了一些import语句 - C++ 代码目录可参考A6
Python 源码目录节选
torch/ao/
- nn/
- intrinsic/
- modules/
- qat/modules/
- quantized/
- modules/
- dynamic/modules/
- qat/
- modules/
- dynamic/modules/
- quantizable/modules/ # 似乎不在下面的模块缩写中??
- quantized/
- modules/
- dynamic/modules/
- reference/modules/
- functional.py
- quantization/
- fx/
- quantize.py
- quantize_fx.py
- qconfig.py
- qconfig_mapping.py
- observer.py
- ...
涉及 Module 的模块位置
关于 Module 的缩写及源码位置总结如下, 具体看下表
- 新位置为 torch.ao.nn[.xxx], 对应原位置为 torch.nn[.xxx]
- torch.ao.nn.intrinsic 目录底下都是 fused layer 相关的东西, 而 torch.ao.nn.[qat,quantized] 目录底下都是对应
nn.Linear,nn.Conv2d的 layer - torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic 不支持 Conv2d
- 缩写规则如下:
nn: torch.ao.nni: intrinsicq: quantizedqat: qatr: reference
- 在后面所绘制的 workflow 图里, 只有
nnqr与nnqatd没有被使用到 (这两个模块待后续研究)
| 模块名缩写 (torch/ao/quantization/quantization_mapping.py) | 模块名 (迁移后: torch.ao) | 模块名 (迁移前: torch.quantization) |
|---|---|---|
| nni | torch.ao.nn.intrinsic[.modules.fused.LinearReLU] | torch.nn.intrinsic[.modules.fused.LinearReLU] |
| nniq | torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] | torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] |
| nniqd | torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] | torch.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] |
| nniqat | torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] | torch.nn.intrinsic.qat[.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU] |
| nnq | torch.ao.nn.quantized[.modules.conv.Conv2d] | torch.nn.quantized[.modules.conv.Conv2d] |
| nnqr | torch.ao.nn.quantized.reference[.modules.conv.Conv2d] | torch.nn.quantized.reference[.modules.conv.Conv2d] |
| nnqd | torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic[.modules.conv.Conv2d] | torch.nn.quantized.dynamic[.modules.conv.Conv2d] |
| nnqat | torch.ao.nn.qat[.modules.conv.Conv2d] | torch.nn.qat[.modules.conv.Conv2d] |
| nnqatd | torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic[.modules.linear.Linear] | torch.nn.qat.dynamic[.modules.linear.Linear] |
| nnqa | torch.ao.nn.quantizable[.modules.rnn.LSTM] | torch.nn.quantizable[.modules.rnn.LSTM] |
上层 API
这些接口是面向用户的主要接口
- torch.ao.quantization.quantize: static quantization
- torch.ao.quantization.quantize_dynamic: dynamic quantization
- torch.ao.quantization.quantize_qat: QAT
- torch.ao.quantization.prepare: static quantization
- torch.ao.quantization.prepare_qat: QAT
- torch.ao.quantization.convert: static quantization/QAT
这些接口的关系可以用下面的伪代码来描述 (注意省略了一些使用细节, 仅仅是框架):
# dynamic quantization
qmodel = quantize_dynamic(model, ...)
# static quantization
# 方法一: 实质上与方法二等价
qmodel = quantize(model, fn, ...)
# 方法二:
fp_model = prepare(model, fn, ...) # fp_model 依然是 float 类型的模型
fn(fp_model, ...) # 校准数据喂入模型
qmodel = convert(fp_model)
# QAT
# 方法一: 实质上与方法二等价
qmodel = quantize_qat(model, fn, ...)
# 方法二:
fp_model = prepare_qat(model, fn, ...) # fp_model 依然是 float 类型的模型
fn(fp_model, ...) # 校准数据喂入模型
qmodel = convert(fp_model)
底层 API
TODO: 本节与前面的重复度太高
以下是具体的 API 总结, 省略了 torch.ao 前缀, 大致浏览即可, 大部分与 Module 相关的前面已经介绍过.
- 公共部分:
- quantizad tensor (感觉暴露的接口/文档并不完善): Tensor.dequantize, Tensor.q_scale, Tensor.q_zero_point, Tensor.int_repr, torch.quantize_per_tensor, torch.dequantize, torch.quantize_per_tensor_dynamic
- observer (观测输入输出浮点值的分布): quantization.observer.MinMaxObserver, quantization.observer.default_observer
- QConfig (量化配置, 例如 int8/uint8, 对称量化/非对称量化): torch.per_tensor_affine, quantization.qconfig.QConfig, quantization.qconfig.default_dynamic_qconfig
- dynamic quantization:
- 量化后的 int layer: nn.quantized.dynamic.Linear
- 量化后的 fused int layer: nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic.LinearReLU
- static quantization / QAT:
- 调用
prepare_model之前的准备工作: fuse_modules, QuantStub - 量化后的 int layer: nn.quantized.Linear
- 量化后的 fused int layer: nn.intrinsic.quantized.ConvReLU2d
- 量化后的 int layer 函数式接口: nn.quantized.functional.conv2d
- 量化算子 (没有记录在文档上的接口): torch.ops.quantized.conv2d
- 调用
- static quantization:
- 调用
prepare_model之后的 fused float layer: nn.intrinsic.ConvReLU2d
- 调用
- QAT:
- 伪量化层: quantization.fake_quantize.FakeQuantize
- 调用
prepare_model之后的 fused float layer: nn.intrinsic.qat.ConvReLU2d - 调用
prepare_model之后的 float layer: nn.qat.Linear
其他:
- nn.qat.dynamic.Linear: 不确定
- nn.quantizable.LSTM, nn.quantizable.MultiheadAttention: static/QAT
prepare_model之后的 layer
这些上层 API 与底层 API 之间的联系在官方文档中解释和代码示例中里解释的比较清楚, 也可以直接参考后文对上层接口的具体介绍
- A3-post-training-dynamic-quantization: dynamic quantization 原理
- A3-post-training-static-quantization: static quantization 原理
- A3-quantization-aware-training-for-static-quantization: QAT 原理
- A3-quantization-custom-module-api: 自定义量化教程, 也一定程度上解释了上层 API 与底层 API 间的联系
下面会先具体介绍一下底层接口, 之后再分章节从上层接口的官方使用示例作为源码分析目标, 介绍各个量化算法的具体流程及相应的实现方式.
底层接口
本节只介绍一部分底层接口, 其余底层接口与具体的量化算法结合起来在后续章节介绍.
quantized tensor
(TODO: 这句话需要调整一下) pytorch 文档中对量化的具体数学公式及针对量化张量的算子没有十分仔细的描述, 对公式感兴趣的读者仔细研究这个博客 A7
Pytorch 的核心量化公式是:
\[\begin{align*} Xq &= round(\frac{x}{s}) + Z \quad (quantization)\\ \tilde{x}&=(Xq - Z) * s \quad (dequantization) \end{align*}\]其中 $x$ 是原始的浮点数值, $Xq$ 是量化后的整数值, $\tilde{x}$ 是量化-反量化后的浮点数值, $Z$ 是浮点数 $0.0$ 量化后的整数值 (从量化公式上看, 浮点数 $0.0$ 经过量化-反量化后会是无损的), $s$ 是浮点数放缩因子
接下来简单看下一些关于 quantized tensor 的底层 API, 主要参考资料: A6, A2
quantized tensor 的创建
x = torch.tensor([-1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 20])
qx = torch.quantize_per_tensor(x, scale=0.1, zero_point=10, dtype=torch.qint8)
print(qx)
print("int8 represent", torch.int_repr(qx)) # 获取 int8 数据, qx = (x / s + zero) = x / 0.1 + 10, qx.int_repr() 也 OK
print("dequantized data", qx.dequantize()) # 反量化回 float 类型
qx.q_scale() # 0.1
qx.q_zero_point() # 10
qx.qscheme() # torch.per_tensor_affine
# tensor([-1.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 11.7000], size=(4,), dtype=torch.qint8,
# quantization_scheme=torch.per_tensor_affine, scale=0.1, zero_point=10)
# int8 represent tensor([ 0, 10, 20, 127], dtype=torch.int8)
# dequantized data tensor([-1.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 11.7000])
quantized tensor 算子 (TODO)
- 算子:
torch.ops.quantized, 例如:torch.ops.quantized.linear_dynamic, 这类 API 都没有被记录在 Pytorch 文档上, 可以通过查看相应 Module 的 forward 函数来观察 - nn.Module:
- functional:
- quantized tensor 方法:
x = torch.randn(2, 3) # (B, in)
scale, zero_point = 1e-4, 2
dtype = torch.quint8
x = torch.quantize_per_tensor(x, scale, zero_point, dtype)
w = torch.randn(4, 3) # (out, in)
scale, zero_point = 1e-3, 2
dtype = torch.qint8
w = torch.quantize_per_tensor(w, scale, zero_point, dtype)
torch.ao.nn.quantized.functional.linear(x, w)
observer
observer 的作用主要是确定原始浮点数据的 min_val 和 max_val, 并依据量化后整数数值范围计算好放缩系数及“整数零”, 代码主要位于 torch/ao/quantization/observer.py 下, 以下示例参考A1
# 备注: 后续版本 pytorch 的源码计划由 torch/quantization -> torch/ao/quantization
from torch.ao.quantization.observer import MinMaxObserver, MovingAverageMinMaxObserver, HistogramObserver
C, L = 3, 4
normal = torch.distributions.normal.Normal(0,1)
inputs = [normal.sample((C, L)), normal.sample((C, L))]
observers = [MinMaxObserver(), MovingAverageMinMaxObserver(), HistogramObserver()]
for obs in observers:
for x in inputs:
obs(x) # MinMaxObserver 这些类实际上继承自 nn.Module
print(obs.__class__.__name__, obs.calculate_qparams())
torch/ao/quantization/observer.py 还包含了许多内部使用的 default_*_observer 的定义, 例如:
# Default weight observer.
default_weight_observer = MinMaxObserver.with_args(dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_symmetric)
# Symmetric weight observer with the 8-bit values restricted to [-127, +127], excluding -128.
weight_observer_range_neg_127_to_127 = MinMaxObserver.with_args(
dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_symmetric,
quant_min=-127, quant_max=127, eps=2 ** -12)
# Default observer for dynamic quantization.
default_dynamic_quant_observer = PlaceholderObserver.with_args(
dtype=torch.quint8, quant_min=0, quant_max=255, is_dynamic=True,
)
# ...
qschema, QConfig, observer
伪代码如下
# 一般情况下 reduce_range 是 False, quant_min 和 quant_max 由 dtype 及 reduce_range 确定
observer = Observer(
dtype=torch.quint8,
qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine, # 枚举类型
reduce_range=False, # 含义参见 https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/what-is-the-purpose-of-reduce-range/163291
quant_min=None, # -128
quant_max=None, # 127
)
# QConfig 通常用于高阶 API (即直接指定带量化的完整模型的量化选项)
# torch/ao/quantization/qconfig.py
default_dynamic_qconfig = QConfig(
activation=default_dynamic_quant_observer,
weight=default_weight_observer
)
关于 reduce_range 参数, 可参见这里, 简单来说:
# torch.qint8
quant_min, quant_max = -128, 127 # reduce_range=False
quant_min, quant_max = -64, 63 # reduce_range=True
# torch.quint8
quant_min, quant_max = 0, 255 # reduce_range=False
quant_min, quant_max = 0, 127 # reduce_range=True
# torch.qint32
quant_min, quant_max = -1 * (2 ** 31), (2 ** 31) - 1 # reduce_range=False
quant_min, quant_max = 0, 15 # reduce_range=True
FakeQuantize
关键的底层 OP 实际上是 torch.fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine
x = torch.tensor(10.23) # (-14.85, 10.75) 的范围内, qx 对 q 的梯度为 1.0
scale = torch.tensor([0.1], dtype=torch.float) # pytorch 的实现里不能对 scale 求导, scale 完全是由观测值确定的
x.requires_grad = True
# scale.requires_grad = True
# RuntimeError: The function '_fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine_cachemask_tensor_qparams' is not differentiable with respect to argument 'scale'. This input cannot have requires_grad True.
zero_point = torch.tensor([20], dtype=torch.int)
qx = torch.fake_quantize_per_tensor_affine(x, scale, zero_point, -128, 127)
qx.sum().backward()
print(f"x: {x}, quantized x: {qx}, grad: {x.grad.item()}")
(Highlight, Ready) 上层接口
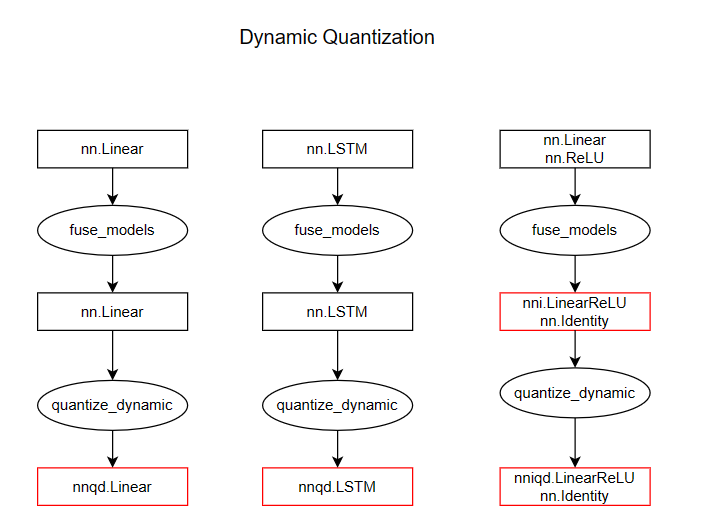
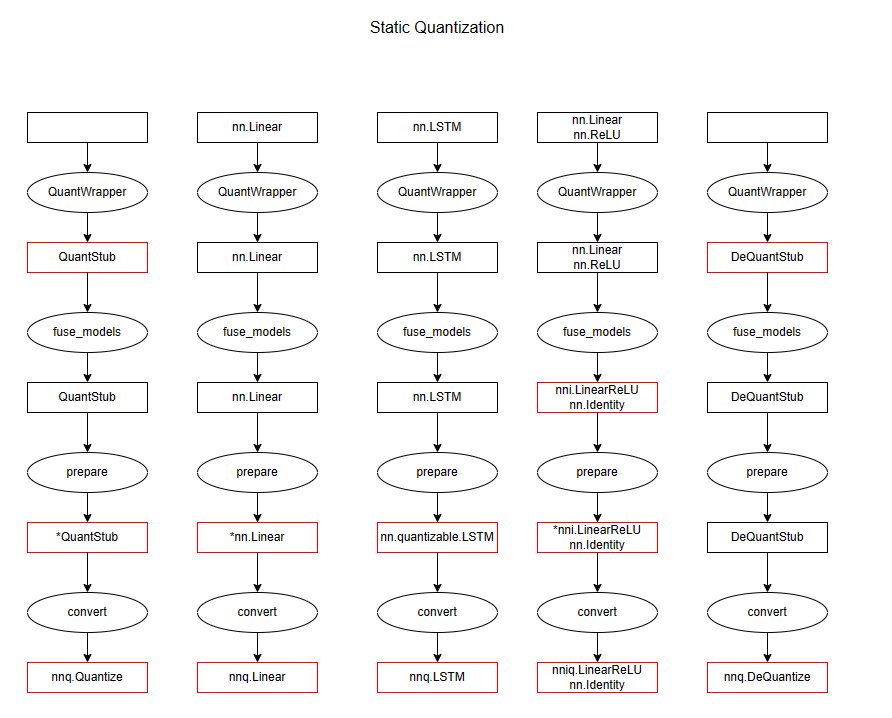
本节内容实际上是下面几节代码分析的总纲, 3 种量化涉及到几个上层 API 实际上就是对需要被量化的每一个子模型进行一对一转换, 这里先给出整个 workflow 过程中 layer 的变化, 对应的代码见本节后文, 我们这里关注 QuantStub, nn.Linear, nn.LSTM, nn.Linear+nn.ReLU, DeQuantStub, 这也涵盖了前面所提到的大多数 Module 类. 下面的示意图表示了每个上层 API 的输入与输出
dynamic quantization
static quantization
QAT
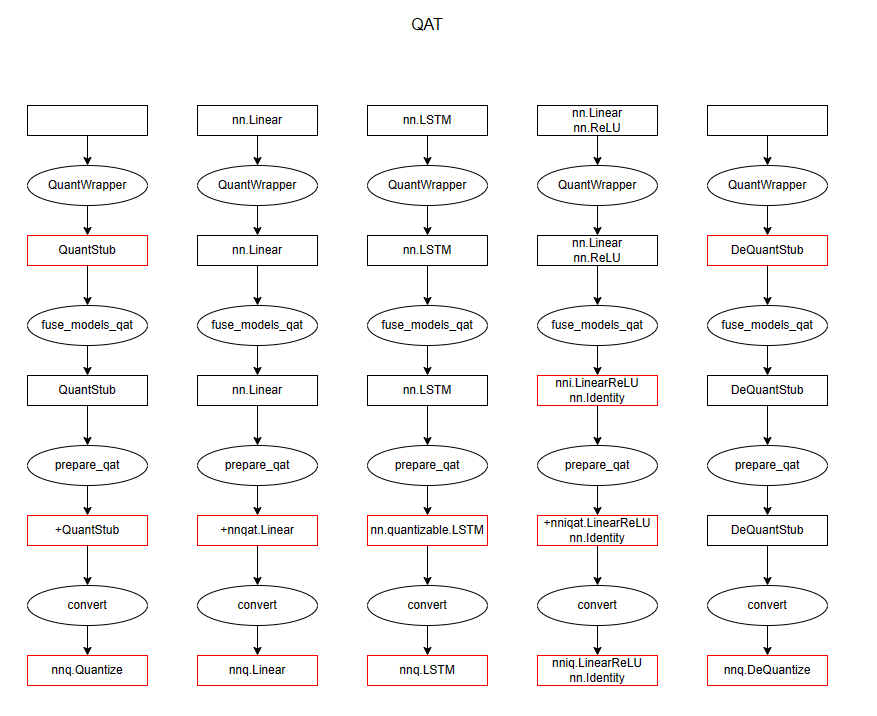
关于上述的符号 * 和 + 的解释:
static quantization (对应于符号 * ): 在 prepare 之后, 对于一个layer
- 如果 layer 需要被量化或是 QuantStub 层, 那么它包含以下属性
- activation_post_process: ObserverBase, 它被注册为 layer 的 forward_hook, 用于观测 layer 层输出的取值范围
- 如果 layer 是 DeQuantStub, 那么它什么都不包含
- 如果 layer 无需量化, 则全流程保持为普通的 float 形式的 nn.Module, 且不会追加任何 hook 或子模块
qat (对应于符号 + ): 在 prepare_qat 之后, 对于一个layer
- 如果 layer 需要被量化, 那么它包含如下属性
- weight_fake_quant: FakeQuantizeBase, 在 layer 的 forward 函数中被调用, 用于对权重的量化与反量化
- weight_fake_quant.activation_post_process: ObserverBase, 在 layer.weight_fake_quant 的 forward 函数中被调用, 用于观测权重的取值范围
- activation_post_process: FakeQuantizeBase, 被注册为 layer 的 forward_hook, 用于对 layer 层输出进行量化与反量化
- activation_post_process.activation_post_process: ObserverBase, 在 layer.activation_post_process 的 forward 函数中被调用, 用于观测 layer 层输出的取值范围
- 如果 layer 是 QuantStub, 那么它只包含 activation_post_process 和 activation_post_process.activation_post_process
- 如果 layer 是 DeQuantStub, 那么它什么都不包含
- 如果 layer 无需量化, 则全流程保持为普通的 float 形式的 nn.Module, 且不会追加任何 hook 或子模块
使用示例参考 A1, A2, A3, 这份 代码 汇总了一下如下简单的模型的量化过程, 也对应了上面的流程图.
m = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2, 64, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(64, 64),
nn.Linear(64, 10), # 手动指定与接下来的 relu 融合
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LSTM(10, 10)
)
结果如下:
<<<dynamic quantization>>>
origin_float32_model fused_float32_model dynamic_quantized_int8_model
-------------------------------- ---------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------
torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU
torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules.fused.LinearReLU torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity
torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.rnn.LSTM
<<<static quantization>>>
origin_float32_model wrapped_float32_model fused_float32_model fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model static_quantized_int8_model
-------------------------------- --------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------------------
<placeholder> torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub *torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.Quantize
torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d *torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.conv.Conv2d
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU
torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear *torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear.Linear
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules.fused.LinearReLU *torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules.fused.LinearReLU torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity
torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.ao.nn.quantizable.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.rnn.LSTM
<placeholder> torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.DeQuantize
<<<qat static quantization>>>
origin_float32_model wrapped_float32_model fused_float32_model fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model qat_static_quantized_int8_model
-------------------------------- --------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------------------
<placeholder> torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub +torch.ao.quantization.stubs.QuantStub torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.Quantize
torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d +torch.ao.nn.qat.modules.conv.Conv2d torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.conv.Conv2d
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU
torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear +torch.ao.nn.qat.modules.linear.Linear torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear.Linear
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules.fused.LinearReLU +torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.qat.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.quantized.modules.linear_relu.LinearReLU
torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity
torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.ao.nn.quantizable.modules.rnn.LSTM torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.rnn.LSTM
<placeholder> torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.quantization.stubs.DeQuantStub torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.DeQuantize
下面几节将深入各类量化方法的细节, 大体思路如下:
Dynamic Quantization:
- 用法 (OK)
- 量化后的 Linear 层是怎样运算的 (OK)
- 量化后的 ReLU 层是怎样运算的 (TODO)
- 量化后的 fusion 层是怎样运算的 (TODO) Static Quantization:
- 用法 (OK)
- 量化后的 Linear 层是怎样运算的 (OK)
- 量化后的 ReLU 层是怎样运算的 (TODO)
- 量化后的 fusion 层是怎样运算的 (TODO) QAT:
- 用法 (TODO)
prepare_qat与训练阶段的运算逻辑 (TODO)
备注: QAT 的推理逻辑与 Static Quantization 相同, 无需赘述
备注: 以下章节的基本原理读者直接参考A7, 笔者更侧重于对齐 Pytorch: 手工实现来验证理解的准确性, 但比较混乱, 且内容不如A7 完善. 因此读者可跳过以下所有内容, 直接阅读A7 即可
(Alpha) Dynamic Quantization
使用方式
涉及如下 3 个高级 API:
- eager mode:
torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic - fx mode:
torch.quantization.quantize_fx.prepare_fx,torch.quantization.quantize_fx.convert_fx
以下是一个完整的示例, 参考自A1, 运行环境: torch==2.1.0
import torch
from torch import nn
m = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2, 64, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(64, 10),
nn.LSTM(10, 10))
m.eval()
## EAGER MODE
from torch.quantization import quantize_dynamic
model_quantized = quantize_dynamic(
model=m, qconfig_spec={nn.LSTM, nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8, inplace=False
)
## FX MODE
from torch.quantization import quantize_fx
qconfig_dict = {"": torch.quantization.default_dynamic_qconfig} # An empty key denotes the default applied to all modules
model_prepared = quantize_fx.prepare_fx(m, qconfig_dict, torch.rand(32, 2, 8, 8))
model_quantized = quantize_fx.convert_fx(model_prepared)
quantize_dynamic 函数的执行逻辑大体上是遍历每一个层, 如果可以动态量化, 则进行一对一转换, 伪代码如下:
mapping = {
torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear: torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear,
torch.nn.modules.rnn.LSTM: torch.ao.nn.dynamic.modules.rnn.LSTM,
}
mod: torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 5)
new_mod = torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear.from_float(mod) # 一对一转换
# 因此主要就关注 from_float 方法及 forward 方法即可
# torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear.from_float 的具体细节(一个分支)
mod = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10) # out: 64, in: 10
observer = torch.ao.quantization.observer.MinMaxObserver()
observer(mod.weight)
wt_scale, wt_zp = observer.calculate_qparams() # 在 torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.utils._quant_weight 函数中
qweight = torch.quantize_per_tensor(mod.weight.float(), float(wt_scale), int(wt_zp), torch.int8)
qweight = _clamp_weights(qweight, observer, wt_scale, wt_zp) # torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.utils._clamp_weights
qlinear = torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear(mod.in_feature, mod.out_feature, dtype=torch.int8)
qlinear.set_weight_bias(qwight, mod.bias)
# torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear.forward 见下面的分析
after quantize_dynamic: torch.ao.nn.quantized.dynamic.modules.linear.Linear 深入分析
以线性层为例, 来分析一下底层实现, torch==2.0.0 源代码:
# torch/ao/nn/quantized/dynamic/modules/linear.py
class Linear(nnq.Linear): # 父类 nnq.Linear 是 torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear.Linear, 这里不再过多描述
def __init__(self, ...): ...
def forward(self, x): # 我们只看 qint8 的实现: 只支持fp16与qint8
# self._packed_params 是 torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear.LinearPackedParams 对象
# self._packed_params._packed_params 是 torch._C.ScriptObject 对象, 包含了量化后的权重(torch.qint8类型)与偏置(fp32类型)
# 输入: x(float32), 输出: Y(float32)
Y = torch.ops.quantized.linear_dynamic(x, self._packed_params._packed_params, reduce_range=True) # 此算子是 C++ 实现
return Y.to(x.dtype) # 这里是 float -> float 的转换 (也许会出现 fp16 与 fp32 之间的转换?)
# 伪代码刚刚已经分析过, 这里贴上源码
@classmethod
def from_float(cls, mod):
# mod (nn.Module): a float module, either produced by torch.ao.quantization utilities or provided by the user
float_modules = [torch.nn.Linear, torch.nn.modules.linear.NonDynamicallyQuantizableLinear,
torch.ao.nn.intrinsic.modules.fused.LinearReLU, torch.ao.nn.qat.dynamic.Linear]
assert type(mod) in float_modules, 'nn.quantized.dynamic.Linear.from_float only works for one of' + str([float_mod.__name__ for float_mod in float_modules])
assert hasattr(mod, 'qconfig'), 'Input float module must have qconfig defined'
if type(mod) == nni.LinearReLU:
mod = mod[0]
if mod.qconfig is not None and mod.qconfig.weight is not None:
weight_observer = mod.qconfig.weight()
else:
from torch.ao.quantization.qconfig import default_dynamic_qconfig
weight_observer = default_dynamic_qconfig.weight()
dtype = weight_observer.dtype
assert dtype in [torch.qint8, torch.float16], "The only supported dtypes for dynamic quantized linear are qint8 and float16 got: {}".format(dtype)
weight_observer(mod.weight)
if dtype == torch.qint8:
qweight = _quantize_weight(mod.weight.float(), weight_observer)
elif dtype == torch.float16:
qweight = mod.weight.float()
else:
raise RuntimeError('Unsupported dtype specified for dynamic quantized Linear!')
qlinear = cls(mod.in_features, mod.out_features, dtype=dtype)
qlinear.set_weight_bias(qweight, mod.bias)
return qlinear
我们只需要重点关注 from_float (已用伪代码描述过) 和 forward 方法即可, 在此之前先简单看一个小细节: 注意到上面的 self._packed_params 是 LinearPackedParams 对象, 而 self._packed_params._packed_params 是 torch.ScriptObject 对象 (torch.fx 源码中也有出现)
# torch/ao/nn/quantized/modules/linear.py
class LinearPackedParams(torch.nn.Module):
_version = 3
def __init__(self, dtype=torch.qint8):
super().__init__()
self.dtype = dtype
if self.dtype == torch.qint8:
wq = torch._empty_affine_quantized([1, 1], scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.qint8)
elif self.dtype == torch.float16:
wq = torch.zeros([1, 1], dtype=torch.float)
self.set_weight_bias(wq, None)
@torch.jit.export
def set_weight_bias(self, weight: torch.Tensor, bias: Optional[torch.Tensor]) -> None:
if self.dtype == torch.qint8:
self._packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.linear_prepack(weight, bias)
elif self.dtype == torch.float16:
self._packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.linear_prepack_fp16(weight, bias)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Unsupported dtype on dynamic quantized linear!')
def forward(self, x):
return x
# Version 1
# self
# |--- weight : Tensor
# |--- bias : Tensor
#
# Version 2
# self
# |--- weight : Tensor
# |--- bias : Tensor
# |--- dtype : torch.dtype
#
# Version 3
# self
# |--- _packed_params : (Tensor, Tensor) representing (weight, bias)
# of LinearPackedParams
# |--- dtype : torch.dtype
...
我们现在重点搞清 forward 方法中使用到的 torch.ops.quantized.linear_dynamic 的具体算法细节, 它是 C++ 实现的, 首先是怎么找到它的 C++ 源码呢? 根据README.md 的指引, 注意到这两个文件:
// aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/library.cpp
TORCH_LIBRARY(quantized, m) {
// ...
m.def(TORCH_SELECTIVE_SCHEMA("quantized::linear_dynamic(Tensor X, __torch__.torch.classes.quantized.LinearPackedParamsBase W_prepack, bool reduce_range=False) -> Tensor Y"));
m.def(TORCH_SELECTIVE_SCHEMA("_quantized::linear_dynamic(Tensor X, __torch__.torch.classes.quantized.LinearPackedParamsBase W_prepack, bool reduce_range=False) -> Tensor Y"));
// ...
}
// aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qlinear_dynamic.cpp
TORCH_LIBRARY_IMPL(quantized, CPU, m) {
// ...
m.impl(TORCH_SELECTIVE_NAME("quantized::linear_dynamic"), TORCH_FN(QLinearDynamicInt8<false>::run));
// ...
}
TORCH_LIBRARY_IMPL(_quantized, CPU, m) {
// ...
m.impl(TORCH_SELECTIVE_NAME("_quantized::linear_dynamic"), TORCH_FN(QLinearDynamicInt8<false>::run));
}
而对应的最终实现 (仅关注 fbgemm 后端: FaceBook GEneral Matrix Multiplication) 在 aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qlinear_dynamic.cpp 中, 源码, 而它最终会调用 fbgemm 的 fbgemm::fbgemmPacked 函数
Highlight
torch.ops.quantized.linear_dynamic 的执行逻辑如下 (以下源码在这里: fbgemm 后端):
- 首先对输入数据进行量化, 使用最大最小非对称量化, 量化后的数据类型为
uint8 - 分配输出结果的内存空间
output(float32 数组, 源码中可以见到at::kFloat这样的代码) 和计算缓冲空间buffer(int32 数组, 源码中可以见到诸如at::kInt,buffer.data_ptr<int32_t>这样的代码)auto output = at::empty(out_sizes, input.options().dtype(at::kFloat)); auto buffer = at::empty_like(output, output.options().dtype(at::kInt), LEGACY_CONTIGUOUS_MEMORY_FORMAT); // ... return output - 然后调用
fbgemm::fbgemmPacked进行计算: 此算子输入时量化后的输入 (uint8) 与量化权重 (int8) 及偏置 (float32), 输出为 float32 类型, 从以下摘录的源码及注释可以看出, 实际的计算过程是先执行 uint8 与 int8 的矩阵乘法, 计算结果累积在 int32 的buffer上, 然后转换回 float32 到output上, 最后加上 float32 的偏置// C(output) = A(input) x B(weight), where C, A, B are M x N, M x K, K x N matrices, respectively. // Process the per tensor quantization. // // After the uint8 * int8 matrix multiplication is performed, this // operation does: // 1) Add in row and column offsets to the rows and columns, // respectively. // 2) Dequantize the results into floating point. // 3) Add in the bias term. fbgemm::ReQuantizeForFloat<ReluFused> outputProcObj( /*nextop=*/doNothingObj, /*Aq_scale=*/q_params.scale, /*Bq_scale=*/w_scale.data(), /*Aq_zero_point=*/q_params.zero_point, /*Bq_zero_point=*/w_zp.data(), /*row_offsets=*/packA.getRowOffsetBuffer(), /*col_offsets=*/col_offsets.data(), /*bias=*/bias_ptr, /*nCol=*/N); // Do the GEMM fbgemm::fbgemmPacked( /*packA=*/packA, /*packB=*/*packB, /*C=*/output.data_ptr<float>(), /*C_buffer=*/buffer.data_ptr<int32_t>(), /*ldc=*/N, /*outProcess=*/outputProcObj, /*thread_id=*/task_id, /*num_threads=*/num_tasks);
由于继续深入 fbgemm::fbgemmPacked 有些过于琐碎(没能力看懂), 因此这里给出其源码位置与之等价的 python 实现:
实现一: 使用 pytorch quantization 的低阶 API 实现 (完全对齐高阶API)
# from torch.ao.quantization.qconfig import default_dynamic_qconfig
# from torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear import LinearPackedParams
from torch.ao.quantization.observer import MinMaxObserver
from torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.utils import _quantize_weight
from torch.quantization import quantize_dynamic
layer = torch.nn.Linear(4, 10)
x = torch.rand(1, 4)
dtype = torch.qint8
# observer = default_dynamic_qconfig.weight()
observer = MinMaxObserver(dtype=dtype, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_symmetric)
observer(layer.weight)
qweight = _quantize_weight(layer.weight.float(), observer)
# packed_params = LinearPackedParams(dtype)
# packed_params._packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.linear_prepack(qweight, layer.bias)
packed_params = torch.ops.quantized.linear_prepack(qweight, layer.bias) # torch.ScriptObject 对象
# packed_params 有一个 unpack 方法: qweight, bias = packed_params.unpack()
manual_res = torch.ops.quantized.linear_dynamic(x, packed_params, reduce_range=True)
model_quantized = quantize_dynamic(model=torch.nn.Sequential(layer), qconfig_spec={nn.LSTM, nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8, inplace=False)
torch_res = model_quantized(x)
print("高阶API与低阶API的实现差异:", (y1-y2).abs().max().item()) # 0.0
实现二: 使用 pytorch quantization 的部分低阶 API 实现量化张量算子
batch_size, in_features, out_features = 20, 30, 40
model = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features))
qmodel = torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic(model, qconfig_spec={torch.nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8, inplace=False)
x = torch.rand(batch_size, in_features)
# 方法一: 利用高阶 API 计算
y1 = qmodel(x)
# 方法二: 利用低阶 API 计算
qw = qmodel[0].weight() # symmetric=True, torch.qint8, reduce_range=False
# 与高阶API的一致性:
# qlinear_dynamic 的源码(https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v2.0.0/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qlinear_dynamic.cpp#L31) 中使用 quant_utils::ChooseQuantizationParams(...) 来计算输入数据的量化参数
# 而 quantize_per_tensor_dynamic 的源码(https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v2.0.0/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/QTensor.cpp#L17)也是用同样的方式计算
qx = torch.quantize_per_tensor_dynamic(x, dtype=torch.quint8, reduce_range=True) # symmetric=False
intw = qw.int_repr().to(torch.int64).T
intx = qx.int_repr().to(torch.int64)
zw = qw.q_zero_point()
zx = qx.q_zero_point()
sw = qw.q_scale()
sq = qx.q_scale()
y2 = model[0].bias + sw * sq * (intx @ intw - zx * torch.ones_like(intx) @ intw - intx @ (zw * torch.ones_like(intw)) + zx*zw)
# 原始模型(未经量化)的输出
y3 = model(x)
print("高阶API与低阶API的实现差异:", (y1-y2).abs().max().item())
print("量化前与量化后的计算误差:", (y1-y3).abs().max().item())
实现三: 不使用任何 pytorch quantization API 实现张量量化及算子
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.quantization import quantize_dynamic
# =================== linear weight 量化 =========================
# weight: dtype=torch.qint8, symmetric=True, reduce_range=False
# input: 约为: dtype=torch.quint8, symmetric=False, reduce_range=True
def calculate_qparams_linear_weight(weight, dtype=torch.qint8, symmetric=True, reduce_range=False):
# dtype: qint8/quint8, symmetric: False/True
# only support per tensor
min_val, max_val = weight.min(), weight.max()
min_val_neg = torch.min(min_val, torch.zeros_like(min_val)) # 用了 0.0 截断
max_val_pos = torch.max(max_val, torch.zeros_like(max_val)) # 用了 0.0 截断
device = min_val_neg.device
scale = torch.ones(min_val_neg.size(), dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
zero_point = torch.zeros(min_val_neg.size(), dtype=torch.int64, device=device)
if reduce_range:
if dtype == torch.qint8:
quant_min, quant_max = -64, 63
elif dtype == torch.quint8:
quant_min, quant_max = 0, 127
# else: raise ValueError(f"{dtype} not support")
else:
if dtype == torch.qint8:
quant_min, quant_max = -128, 127
elif dtype == torch.quint8:
quant_min, quant_max = 0, 255
# else: raise ValueError(f"{dtype} not support")
if symmetric:
max_val_pos = torch.max(-min_val_neg, max_val_pos)
scale = max_val_pos / (float(quant_max - quant_min) / 2)
# symmetric 情况下, 0.0 的量化表示是 0/128
if dtype == torch.quint8:
zero_point = zero_point.new_full(zero_point.size(), 128)
# elif dtype == torch.qint8:
# zero_point = zero_point.new_full(zero_point.size(), 0)
# else: raise ValueError(f"{dtype} not support")
else:
scale = (max_val_pos - min_val_neg) / float(quant_max - quant_min)
# 注意到这可能会使得 min_val_neg 或 max_val_neg 对应的量化值可能不是 quant_min 或 quant_max
zero_point = quant_min - torch.round(min_val_neg / scale).to(torch.int64) # 必须用 round 取整, 如果直接用 to(torch.int) 会是向 0 取整
zero_point = torch.clamp(zero_point, quant_min, quant_max)
return scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max
def quantize_linear_weight(weight, dtype=torch.qint8, symmetric=True, reduce_range=False):
scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max = calculate_qparams_linear_weight(
weight, dtype=dtype, symmetric=symmetric, reduce_range=reduce_range)
qweight = torch.round(weight / scale).to(torch.int64) + zero_point
qweight = torch.clamp(qweight, quant_min, quant_max)
return qweight
def dequantize_linear_weight(qweight, scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max):
deqweight = (qweight - zero_point).float() * scale
return deqweight
# torch 默认用 symmetric 的方式量化权重
def torch_dynamic_quantize_linear_weight(layer: torch.nn.Linear):
qmodel = quantize_dynamic(model=torch.nn.Sequential(layer), qconfig_spec={nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8, inplace=False)
weight = qmodel[0].weight()
zero_point = weight.q_zero_point() # int scaler
scale = weight.q_scale() # float scalar
qweight = weight.int_repr().long() # int64 tensor
return qweight, scale, zero_point
# 单元测试
def test_linear_weight_quantize(layer: torch.nn.Linear):
dtype = torch.qint8
symmetric = True
weight = layer.weight
scale_m, zero_point_m, _, _ = calculate_qparams_linear_weight(weight, dtype=dtype, symmetric=symmetric)
qweight_m = quantize_linear_weight(weight, dtype=dtype, symmetric=symmetric)
qweight_t, scale_t, zero_point_t = torch_dynamic_quantize_linear_weight(layer)
assert int(zero_point_m) == int(zero_point_t)
assert float(scale_m) - float(scale_t) < 1e-7
assert (qweight_m - qweight_t).abs().sum().item() == 0
# ========================= linear input 量化 ============================
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v2.0.0/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qlinear_dynamic.cpp#L31
# 基本上类似于 quantize_linear_weight: symmetric = False, dtype=quint8, reduce_range=True
# 但 zero_point 和 scale 的计算与weight有所区别 (主要是zero_point会在min_val或max_val里选择进行计算)
# TODO: 为简单起见, 这里忽略 zero_point 的差异, 精确实现要参照上面链接里的源码: auto q_params = quant_utils::ChooseQuantizationParams(...)
def quantize_linear_input(x, dtype=torch.quint8, symmetric=False, reduce_range=True):
return quantize_linear_weight(x, dtype=dtype, symmetric=symmetric, reduce_range=reduce_range)
# ======================== 量化数据的矩阵乘法实现(仅示意) ===========================
def gemm(qweight, qinput, bias, weight_qparams, input_qparams):
# input @ weight.T + bias, qweight(n*k), qinput(m*k), bias(n)
# 计算公式如下:
# deq_x = (q_x - z_x) * s_x, deq_w.T = (q_w.T - z_w.T) * s_w (note: z_x, z_w is matrix)
# output = deq_x @ deq_w.T + bias = s_w * s_x * (q_x @ q_w.T - q_x @ z_w .T- z_x @ q_w.T + z_x@z_w.T) + bias
# 注意在真实的实现里: s_w * s_x, z_x @ q_w.T, z_x@z_w 其实可以提前算好, 只有 q_x @ q_w.T 和 q_x @ z_w 需要计算
m, k = qinput.shape
n = qweight.shape[0]
s_w, z_w = weight_qparams
s_x, z_x = input_qparams
# 这里比较低效, 直接创建了常量张量
z_w = torch.ones_like(qweight) * z_w
z_x = torch.ones_like(qinput) * z_x
# 真正的实现是用 torch.int32 进行累加, 此处为了简单 qweight, qinput, buffer 其实都用了 torch.long 类型
buffer = torch.zeros((m, n), dtype=torch.int64)
output = torch.zeros((m, n), dtype=torch.float32) # 真实实现(fbgemm)用float32类型
buffer += qinput @ qweight.T
buffer -= qinput @ z_w.T # 因为权重采用的是对称量化, 所以 z_w 实际上是 0, 因此可跳过这一部分
buffer -= z_x @ qweight.T # 可提前算好
buffer += z_x @ z_w.T # 可提前算好
output = buffer.double() * s_w * s_x + bias
output = output.to(torch.float32) # 真实实现里, 这里是回到 input.dtype
return output
# 使用 pytorch quantization API 的高级接口
def torch_dynamic_quantization_forward(layer, inp):
# fbgemm: per tensor quantize weight (qint8) and input (quint8)
qmodel = quantize_dynamic(model=torch.nn.Sequential(layer), qconfig_spec={nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8, inplace=False)
output = qmodel(inp)
return output
# 不使用任何 pytorch quantization API 的实现
def manual_dynamic_quantization_forward(layer, inp):
weight = layer.weight
bias = layer.bias
# step 1 权重量化, 参考: torch.ao.quantization.observer.MinMaxObserver, 注意取整的方式(四舍五入 vs 向零取整)
qweight = quantize_linear_weight(weight, symmetric=True)
scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max = calculate_qparams_linear_weight(weight, symmetric=True)
weight_qparams = (scale, zero_point)
# deqweight = dequantize_linear_weight(qweight, scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max)
# step 2 输入量化, 参考: C++ 源码: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v2.0.0/aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/cpu/qlinear_dynamic.cpp#L31
qinput = quantize_linear_weight(inp, dtype=torch.quint8, symmetric=False, reduce_range=True)
scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max = calculate_qparams_linear_weight(inp, dtype=torch.quint8, symmetric=False, reduce_range=True)
input_qparams = (scale, zero_point)
# deqinput = dequantize_linear_weight(qinput, scale, zero_point, quant_min, quant_max)
# step 3 量化后的输入与量化后权重进行计算并还原为 float32, 并加上偏置项
output = gemm(qweight, qinput, bias, weight_qparams, input_qparams)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
batch_size, in_features, out_features = 20, 30, 40
layer = torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features)
inp = torch.distributions.normal.Normal(0, 1).sample((batch_size, in_features))
# 测试权重量化的正确性
test_linear_weight_quantize(layer)
# 测试手工实现与pytorch的差异
torch_output = torch_dynamic_quantization_forward(layer, inp)
manual_output = manual_dynamic_quantization_forward(layer, inp)
print("测试手工实现与pytorch的差异:", (torch_output - manual_output).abs().max().item()) # 1.1920928955078125e-07
Static Quantization
使用方式
以下是一个完整的示例, 参考自A1, 运行环境: torch==2.1.0
import torch
class M(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.quant = torch.ao.quantization.QuantStub() # QuantStub converts tensors from floating point to quantized
self.conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 1)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.dequant = torch.ao.quantization.DeQuantStub() # DeQuantStub converts tensors from quantized to floating point
def forward(self, x):
x = self.quant(x) # manually specify where tensors will be converted from floating point to quantized in the quantized model
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.dequant(x) # manually specify where tensors will be converted from quantized to floating point in the quantized model
return x
model_fp32 = M()
model_fp32.eval() # model must be set to eval mode for static quantization logic to work
model_fp32.qconfig = torch.ao.quantization.get_default_qconfig('x86')
model_fp32_fused = torch.ao.quantization.fuse_modules(model_fp32, [['conv', 'relu']])
model_fp32_prepared = torch.ao.quantization.prepare(model_fp32_fused)
input_fp32 = torch.randn(4, 1, 4, 4)
model_fp32_prepared(input_fp32)
model_int8 = torch.ao.quantization.convert(model_fp32_prepared)
# run the model, relevant calculations will happen in int8
res = model_int8(input_fp32)
torch.ao.quantization.quantize.prepare 浅析
现在先分析一下上层接口 prepare, 源码:
def prepare(model, inplace=False, allow_list=None,
observer_non_leaf_module_list=None,
prepare_custom_config_dict=None):
r"""Prepares a copy of the model for quantization calibration or quantization-aware training.
Quantization configuration should be assigned preemptively
to individual submodules in `.qconfig` attribute.
The model will be attached with observer or fake quant modules, and qconfig
will be propagated.
Args:
`model`: input model to be modified in-place
`inplace`: carry out model transformations in-place, the original module is mutated
`allow_list`: list of quantizable modules
`observer_non_leaf_module_list`: list of non-leaf modules we want to add observer
`prepare_custom_config_dict`: customization configuration dictionary for prepare function
.. code-block:: python
# Example of prepare_custom_config_dict:
prepare_custom_config_dict = {
# user will manually define the corresponding observed
# module class which has a from_float class method that converts
# float custom module to observed custom module
"float_to_observed_custom_module_class": {
CustomModule: ObservedCustomModule
}
}
"""
torch._C._log_api_usage_once("quantization_api.quantize.prepare")
if prepare_custom_config_dict is None:
# 即返回下面的 _DEFAULT_CUSTOM_CONFIG_DICT, 是一个字典的字典, 包含两个 key:
# "float_to_observed_custom_module_class", "observed_to_quantized_custom_module_class"
# 内层字典包含 nn.Module 的映射关系
prepare_custom_config_dict = get_default_custom_config_dict()
custom_module_class_mapping = prepare_custom_config_dict.get("float_to_observed_custom_module_class", {})
if not inplace:
model = copy.deepcopy(model)
# TODO: remove allow_list
qconfig_propagation_list = allow_list
if allow_list is None:
qconfig_propagation_list = get_default_qconfig_propagation_list() # ??? 不确定含义, 是一个集合, 涵盖了 nn.Linear
propagate_qconfig_(model, qconfig_dict=None) # 注意在上面的用例中, 在调用 prepare 之前, 手动对 model.qconfig 进行了赋值
# propagate_qconfig_ 的作用是为 model 的 submodule 递归设置好 qconfig 属性:
# 注意如果在调用 prepare 函数之前就手动给 submodule 赋了不同于 model.qconfig 的值, 那么这些手动赋值将被保留, 不受全局的 model.qconfig 的影响
# sanity check common API misusage
if not any(hasattr(m, 'qconfig') and m.qconfig for m in model.modules()):
warnings.warn("None of the submodule got qconfig applied. Make sure you "
"passed correct configuration through `qconfig_dict` or "
"by assigning the `.qconfig` attribute directly on submodules")
# 给每个需要量化的 layer 追加一个 observer 的 module, 然后给这个 layer 追加上执行 observer 的 forward_hook (或 forward_pre_hook)
_add_observer_(
model, qconfig_propagation_list, observer_non_leaf_module_list,
custom_module_class_mapping=custom_module_class_mapping)
return model
import torch.nn as nn
_DEFAULT_CUSTOM_CONFIG_DICT = {
'float_to_observed_custom_module_class': {
nn.LSTM: nn.quantizable.LSTM, # torch.ao.nn.quantizable.modules.rnn.LSTM
nn.MultiheadAttention: nn.quantizable.MultiheadAttention, # torch.ao.nn.quantizable.modules.activation.MultiheadAttention
},
'observed_to_quantized_custom_module_class': {
nn.quantizable.LSTM: nn.quantized.LSTM, # torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.rnn.LSTM
nn.quantizable.MultiheadAttention: nn.quantized.MultiheadAttention, # torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.activation.MultiheadAttention
}
}
propagate_qconfig_
此函数用于将父 module 的 qconfig 属性传播给子 module (除非子 module 自己设置了 qconfig), 测试代码如下:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
from torch.ao.quantization import propagate_qconfig_, get_default_qconfig, get_default_qat_qconfig
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("./hf_download/gpt2")
default_qconfig = get_default_qconfig()
default_qat_qconfig = get_default_qat_qconfig()
print("default_qconfig activation observer name:", default_qconfig.activation.p.func.__name__) # "HistogramObserver"
print("default_qat_qconfig activate observer name:", default_qat_qconfig.activation.p.func.__name__) # "FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize"
model.qconfig = default_qconfig
model.transformer.h[0].qconfig = default_qat_qconfig
propagate_qconfig_(model)
qconfig_observer_name_dict = {
name: m.qconfig.activation.p.func.__name__ for name, m in model.named_modules()
}
print({n: v for n, v in qconfig_observer_name_dict.items() if v != "HistogramObserver"})
输出:
default_qconfig activation observer name: HistogramObserver
default_qat_qconfig activate observer name: FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize
{'transformer.h.0': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.ln_1': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.attn': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.attn.c_attn': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.attn.c_proj': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.attn.attn_dropout': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.attn.resid_dropout': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.ln_2': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.mlp': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.mlp.c_fc': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.mlp.c_proj': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.mlp.act': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize',
'transformer.h.0.mlp.dropout': 'FusedMovingAvgObsFakeQuantize'}
swap_model
_add_observer_ 本质上会对所有需要被 prepare 函数进行转换的子模块调用 swap_module 函数, 用 new_mod 来替换原本的 mod
def swap_module(mod, mapping, custom_module_class_mapping):
new_mod = mod
if hasattr(mod, 'qconfig') and mod.qconfig is not None:
swapped = False
if type_before_parametrizations(mod) in custom_module_class_mapping:
# 通过 from_observed 转换
new_mod = custom_module_class_mapping[type_before_parametrizations(mod)].from_observed(mod)
swapped = True
elif type_before_parametrizations(mod) in mapping:
qmod = mapping[type_before_parametrizations(mod)]
if hasattr(qmod, '_IS_REFERENCE') and qmod._IS_REFERENCE:
assert mod.qconfig is not None
weight_post_process = mod.qconfig.weight()
weight_post_process(mod.weight)
weight_qparams = get_qparam_dict(weight_post_process)
# 通过 from_float 转换
new_mod = qmod.from_float(mod, weight_qparams)
else:
new_mod = qmod.from_float(mod)
swapped = True
if swapped:
# 这里对 hook 的处理也很有意思: 移除 forward_hook 中的一些内容, 完全保留 forward_pre_hook
# Preserve module's pre forward hooks. They'll be called on quantized input
for pre_hook_fn in mod._forward_pre_hooks.values():
new_mod.register_forward_pre_hook(pre_hook_fn)
# Preserve module's post forward hooks except _observer_forward_hook
# After convert they'll work with quantized output
for hook_fn in mod._forward_hooks.values():
if hook_fn is not _observer_forward_hook:
new_mod.register_forward_hook(hook_fn)
# respect device affinity when swapping modules
devices = _get_unique_devices_(mod)
assert len(devices) <= 1, (
"swap_module only works with cpu or single-device CUDA modules, "
"but got devices {}".format(devices)
)
device = next(iter(devices)) if len(devices) > 0 else None
if device:
new_mod.to(device)
return new_mod
after convert: torch.ao.nn.quantized.modules.linear.Linear 深入分析
与上一节类似, 这里给出 python 的对齐实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.ao.quantization import QuantWrapper
calibration_batch_size, test_batch_size, in_features, out_features = 10, 20, 30, 40
# PART 1: 使用上层 API 进行静态量化
layer = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features)
wrapped_float32_model = QuantWrapper(layer) # children: "quant", "dequant", "module"
wrapped_float32_model.eval()
wrapped_float32_model.qconfig = torch.ao.quantization.get_default_qconfig('x86')
# prepare model: 添加 observer
fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model = torch.ao.quantization.prepare(wrapped_float32_model)
# 送入校准数据使得 observer 观测到每一层激活值的分布
input_fp32 = torch.randn(calibration_batch_size, in_features)
fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model(input_fp32)
# 根据 observer 确定激活值的量化参数, 并量化模型本身的权重
static_quantized_int8_model = torch.ao.quantization.convert(fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model)
# PART 2: 量化后的模型推理
y = torch.randn(test_batch_size, in_features)
gt_out = static_quantized_int8_model(y)
# PART 3: 手工 check 各个环节
observer = qconfig.activation() # HistogramObserver(dtype=torch.quint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine, reduce_range=True, bins=2048, upsample_rate=128)
observer(input_fp32)
scale, zero_point = observer.calculate_qparams()
# TODO: assert scale == gt_scale and zero_point
# gt_scale, gt_zero_point = static_quantized_int8_model.quant.scale, static_quantized_int8_model.quant.zero_point
qy = torch.quantize_per_tensor(y, float(scale), int(zero_point), observer.dtype) # static_quantized_int8_model.quant 的 forward
w_observer = qconfig.weight() # PerChannelMinMaxObserver(ch_axis=0, dtype=torch.quint8, qscheme=torch.per_channel_affine, reduce_range=False)
w_observer(layer.weight)
w_scale, w_zero_point = w_observer.calculate_qparams() # w_scale: (out_features,), w_zero_point: (out_features, )
# TODO: assert w_scale == gt_w_scale and w_zero_point == gt_w_zero_point
# gt_qweight, gt_bias = torch.ops.quantized.linear_unpack(static_quantized_int8_model.module._packed_params._packed_params)
# gt_w_scale, gt_w_zero_point = gt_qweight.q_per_channel_scales(), gt_qweight.q_per_channel_zero_points()
out_scale, out_zero_point = fused_float32_prepared_fp32_model.module.activation_post_process.calculate_qparams()
# 两者一样:
# out_scale, out_zero_point = static_quantized_int8_model.module.scale, static_quantized_int8_model.module.zero_point
# aten/src/ATen/native/quantized/library.cpp
# m.def(TORCH_SELECTIVE_SCHEMA("quantized::linear(Tensor X, __torch__.torch.classes.quantized.LinearPackedParamsBase W_prepack, float Y_scale_i, int Y_zero_point_i) -> Tensor Y"));
# qy: quantized tensor, out_scale: float, out_zero_point: int64
out = torch.ops.quantized.linear(qy, static_quantized_int8_model.module._packed_params._packed_params, out_scale, out_zero_point) # static_quantized_int8_model.module 的 forward
# 解开 torch.ops.quantized.linear 的内部细节
def manual_static_quantized_linear(qx, packed_params, out_scale: float, out_zero_point: int):
w, bias = torch.ops.quantized.linear_unpack(packed_params)
x_s, x_z = qx.q_scale(), qx.q_zero_point() # 不适用于 per_channel
w_s, w_z = w.q_per_channel_scales(), w.q_per_channel_zero_points() # w_s: float64
# x @ w.T: (B, in) x (in, out)
w_int = w.int_repr().long()
x_int = qx.int_repr().long()
# out_float = x @ w.T = x_s * (x_int - x_z) * (w_int.T - w_z) @ diag(w_s) # w_s 和 w_z 是向量
# out_float = out_scale * (out_int - out_zero_point)
print(w_int.T.shape, w_z.shape, bias.shape, x_s, w_s)
# 此处不是太确定累积类型是用 float32 还是 float64
out_float = ((x_int - x_z) @ ((w_int.T) - w_z)).double() @ (x_s * torch.diag(w_s)) + bias
q_out = torch.quantize_per_tensor(out_float.float(), out_scale, out_zero_point, dtype=torch.quint8) # 与 qx.dtype 保持一致?
return q_out
manual_out = torch.ops.quantized.linear(qy, static_quantized_int8_model.module._packed_params._packed_params, out_scale, out_zero_point)
# 验证 OP 实现
assert (out.int_repr() - manual_out.int_repr()).abs().sum() == 0
out = out.dequantize() # static_quantized_int8_model.dequant 的 forward
# 验证端到端推理无误
(out - gt_out).abs().max()
QAT (pytorch)
after prepare_qat: torch.ao.nn.qat.modules.linear.Linear 浅析
这个 layer 是经过 prepare_qat 转换后的 float layer, 我们重点关注 forward 函数: 根据前面的描述, 它实际上还带着一个 forward_hook, 这个 hook 会对输出进行量化-反量化操作, 注意在 forward 函数中我们没有看到对输入进行量化-反量化操作 (可以理解成上一层的输出已经做了, 或者如果有必要 prepare_qat 也会注册 forward_pre_hook 来完成这件事, 待确认).
from torch.ao.nn.intrinsic import LinearReLU
class Linear(nn.Linear):
_FLOAT_MODULE = nn.Linear
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=True,
qconfig=None, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype}
super().__init__(in_features, out_features, bias, **factory_kwargs)
assert qconfig, 'qconfig must be provided for QAT module'
self.qconfig = qconfig
self.weight_fake_quant = qconfig.weight(factory_kwargs=factory_kwargs)
def forward(self, input):
return F.linear(input, self.weight_fake_quant(self.weight), self.bias)
@classmethod
def from_float(cls, mod):
r"""Create a qat module from a float module or qparams_dict
Args: `mod` a float module, either produced by torch.ao.quantization utilities
or directly from user
"""
assert type_before_parametrizations(mod) == cls._FLOAT_MODULE, (
" qat."
+ cls.__name__
+ ".from_float only works for "
+ cls._FLOAT_MODULE.__name__
)
assert hasattr(mod, "qconfig"), "Input float module must have qconfig defined"
assert mod.qconfig, "Input float module must have a valid qconfig"
if type_before_parametrizations(mod) == LinearReLU:
mod = mod[0]
qconfig = mod.qconfig
qat_linear = cls(mod.in_features, mod.out_features, bias=mod.bias is not None, qconfig=qconfig)
if is_parametrized(mod, "weight"):
transfer_parametrizations_and_params(mod, qat_linear, "weight")
else:
qat_linear.weight = mod.weight
if is_parametrized(mod, "bias"):
transfer_parametrizations_and_params(mod, qat_linear, "bias")
else:
qat_linear.bias = mod.bias
return qat_linear
def to_float(self):
linear = torch.nn.Linear(self.in_features, self.out_features, self.bias is not None)
linear.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(self.weight.detach())
if self.bias is not None:
linear.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(self.bias.detach())
linear.train(self.training)
return linear
QAT (tensorflow)
参考 Release 列表, 相关版本: tensorflow==2.0.0, model_optimization==0.3.0
# tensorflow_model_optimization/python/core/quantization/keras/quantize.py
def quantize_model(to_quantize: tf.keras.Model):
def _add_quant_wrapper(layer):
return quantize_annotate_mod.QuantizeAnnotate(layer)
annotated_model = tf.keras.models.clone_model(to_annotate, input_tensors=None, clone_function=_add_quant_wrapper)
return quantize_apply(annotated_model)